Designing Interactions for Motor Learning
The number of HCI papers relating to procedural memory, muscle memory, and motor learning has increased significantly in the last couple of decades, showing that HCI is incorporating technical developments such as motion capture systems and augmented and virtual reality to investigate the design of systems that engage with motor memory. However, there remains no clear understanding of:
a) What methods and technology are utilized to create systems that engage with motor memory? and,
b) What can be the approaches to design haptic-based systems that engage with motor memory?
Asymmetrical Hand Gestures
We want to investigate if an EMS based system can aid learning of asymmetric hand gestures, compared to learning without such assistance.
skillab
We want to see if EMS may aid in the improvement of motor skills in the context of craftwork using Augmented Reality.
just dance
We want to find out if haptic-supported learning of motoric tasks, demonstrated in the example of dancing, can reduce the training time, compared to skill acquisition. We want to compare EMS and vibrotactile feedback and compare the learning curves.
EMS for human robot interaction
Human must intervene to guide or correct the robot's behavior, such as when the robot gets stuck or fails to accomplish a given job. When there is no direct line of sight to the robot (e.g., the robot is on the other side of a wall), it is more difficult for the human to understand the robot's surroundings in order to provide appropriate guidance. Using EMS, how to avoid colliding with an obstacle that is outside the robot's own field of view when manually controlling the robot?
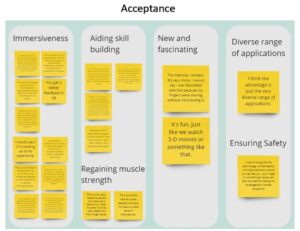

User Acceptance of EMS
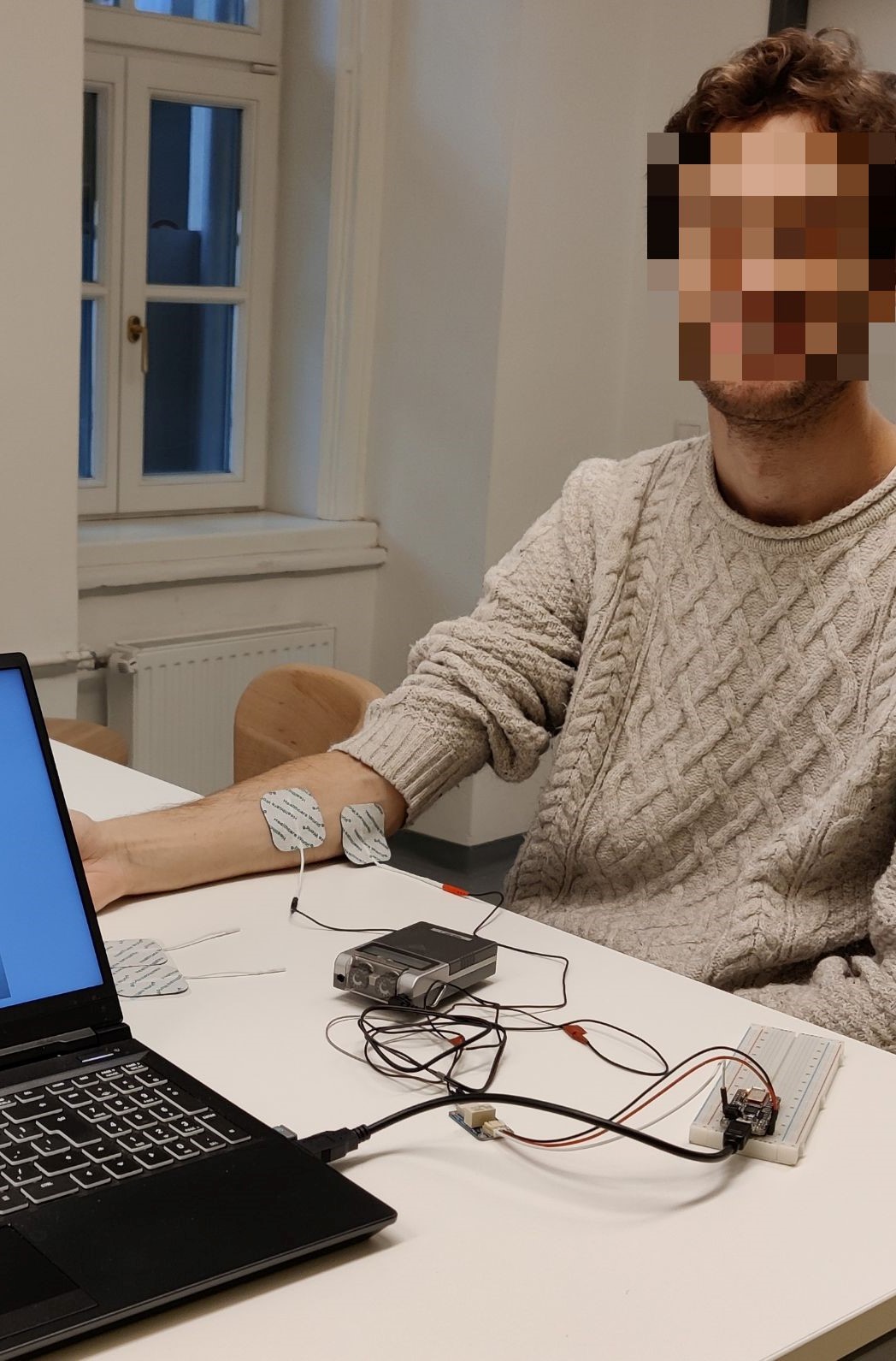
Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS) provides multiple interaction possibilities in various fields. It may transmit object affordances, user motions or give rich haptic feedback by adjusting stimulation settings, especially in virtual worlds. Parameters necessary to accept EMS, impacting how users perceive the technology, are yet not thoroughly studied. We investigated users’ acceptance of EMS by conducting an online survey (N=113) and an interview (N=5) study using four scenarios derived from the literature. We used the technology acceptance paradigm (TAM) to assess user acceptance and gathered factors for accepting/rejecting the technology. By connecting survey results and participants’ impressions of the four EMS scenarios to emerging themes, we can show that potential users reject EMS systems if they perceive a high level of risk and a lack of the sense of agency. We drew inferences based on our findings that will guide in designing and developing products that provide acceptable experiences.

Predoc researcher
ambika shahu
My research interest is in understanding how our bodies and memories work together to develop new motor skills. I am investigating whether or not haptic feedback (EMS and vibrotactile) can be used to teach a new skill. How these interactions can make a more direct and personal connection to our bodies? How can they be both seamless and efficient?
Our
Students

bachelor
Sonja
She focuses on skill development through the use of augmented reality and muscle actuation.

masters
Fabian
He is employing smartwatches and physiological sensor data to aid in digital detox and to limit users’ phone screen time.

bachelor
hanna
She is focusing on finding whether muscle stimulation can aid in the learning of new motoric activities.

bachelor
Christina
She is researching which feedback modality works best for human-robot collaboration in order to enhance the efficiency of overall task performance in dual tasks.

bachelor
Alexander
He is focusing on promoting self-regulation of online news consumption through the use of digital nudges for detox.

masters
Ernad
He is investigating which strategies an app assistant should employ in order to support students in their transition to a digital detox-oriented lifestyle.

bachelor
Jovan
He concentrates on the motor learning of asymmetrical hand gestures using electrical muscle stimulation.

masters
Marino
He works on digital detox, which focuses on more purposeful usage of digital devices (smartphones, tablets, laptops, television) with the objective of enhancing self-control.